How Does Cosmos ($ATOM) Work?

Cosmos ($ATOM) Network is a decentralized network of interoperable & scalable blockchains that run in parallel without losing their sovereignty. It solves the problem of blockchain isolation and creates a more connected ecosystem. Cosmos uses Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol to enable inter-blockchain communication. In simple words IBC lets blockchains talk to each other. This protocol can be used and implemented by other blockchains and app developers to solve the problem of interoperability. If you want to know more, please check out this basic Cosmos ($ATOM) guide to get you started!
In this blog, we are going to see the different components of Cosmos Network and how they work together. Cosmos Network consists of three layers and each of them has different functions and features to support the network.
Cosmos Architecture
The blockchain on Cosmos can be divided into three layers which help in the completion of transactions and reach consensus:
Consensus Layer: Blockchains in the Cosmos network use the Tendermint consensus algorithm. It helps nodes agree on the current state of the network. Using Tendermint BFT engine developers can build their own customized blockchains without making much coding effort. It packs the Networking & Consensus layer into a generic engine so that devs can focus only on the development of the application layer. The algorithm is Byzantine Fault-Tolerant and uses Proof of Stake to secure the network. Validators are the nodes that produce blocks and help the network achieve consensus. They receive fees & block rewards for doing this job round the clock. The system randomly selects validators and two-thirds of these nodes are required to confirm the transaction.
Networking Layer: In order to reach a consensus, nodes must be interconnected with each other. They pass on transactional data and consensus-related messages via Networking Layer. A node does not have to validate blocks in order to send data to other nodes so that everyone sees the most recent data.
Application Layer: In order to validate transactions on the consensus layer, we first need to have a set of transactions. The application layer defines and submits these transactions to get committed by the consensus layer and once that is done, it updates the current state of the blockchain.
Cosmos SDK
Cosmos SDK (Software Development Kit) is used to develop the applications on top of Tendermint BFT. The Tendermint BFT engine is connected to the application layer by a socket protocol called the Application Blockchain Interface (ABCI). Through Cosmos SDK anyone can build their own ABCI App without compromising the security.

The major feature of Cosmos SDK is that it allows anyone to add application-specific modules which can be used by other developers to save on their development time of the application layer. This feature will come in handy once the Cosmos developer community gets bigger. There will be enough modules to build more complicated solutions to real-life problems.
For example, any existing blockchain code written in Golang can be moved into a Cosmos SDK module. Ethermint is a project that replicates the EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) into an SDK module that works exactly like Ethereum. Developers can easily create Cosmos-based modules of their existing Ethereum smart contracts without additional work. Ethermint also benefits from all the properties of Tendermint BFT. Developing on Cosmos gives more flexibility, security, performance, and sovereignty over Ethereum.
Inter Blockchain Communication (IBC)
The main goal of Cosmos is to allow developers to create bridges between various blockchains built on it and outside of Cosmos too i.e full grade interoperability. Inter Blockchain Communication protocol is used to achieve this important feature that creates the Internet of Blockchains. After creating custom blockchains for their DApps using Cosmos SDK, devs can connect them with other blockchains allowing the transfer of Tokens and Data.
IBC also allows bridges between private and public blockchains making it the most powerful interoperability protocol out there. Let's take an example to see how IBC works via Escrow account transfer to avoid loss of funds during transaction failure. Let's suppose an account on Chain 1 wants to send 1 $ATOM to an account on Chain 2:
- Tracking: Chain 2 will receive headers of Chain 1 and vice versa. This establishes the connection between the two chains because they start running a virtual copy of each other to track the transactions.
- Bonding: Once the connection is established, 1 $ATOM will be bonded on Chain 1.
- Proof Relay: A proof of bonding will be propagated (relayed) to Chain 2.
- Validation: Once the proof is validated, bonded $ATOM on Chain 1 gets a representation on Chain 2. Chain 1 will keep those ATOM bonded until their representative $ATOMs on chain 2 are sent back.
Cosmos Hub and Zones
Cosmos follows a modular architecture (Hub & Spoke topology) to create a network of heterogeneous blockchains. Zones are the application specific blockchains which are connected directly to a Hub. Each Hub is connected to other Hubs and multiple zones. Hubs are only made to connect other Hubs and Zones. Each zone has an indirect connection to all the other zones connected to the main Hub. This reduces the no. of connections made as the network expands to thousands of blockchains. Anyone is free to create hubs and zones. The first HUB created on Cosmos is called Cosmos Hub. It can be forked by anyone to create other Tier 1 and Tier 2 Hubs.
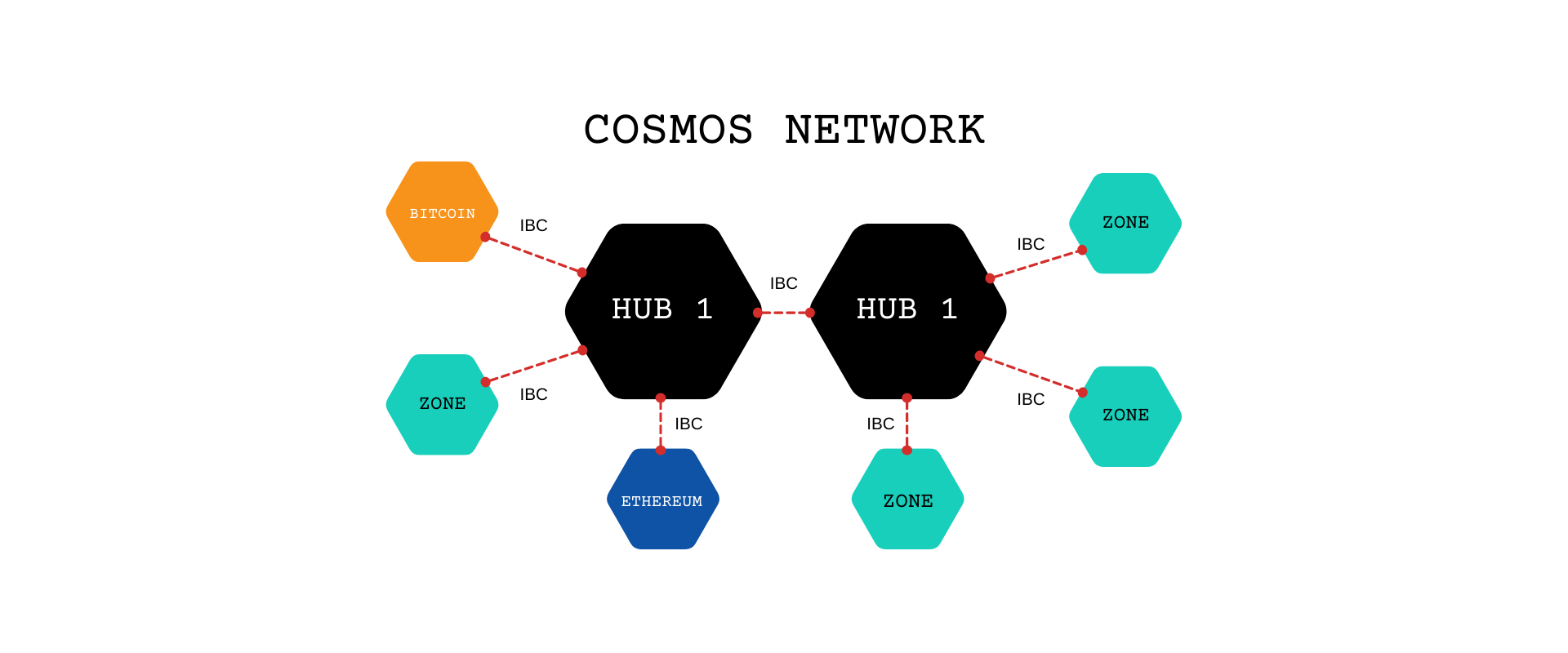
What Is A Peg Zone?
Cosmos Hub & Zone model as well as IBC collectively come together to provide interoperability among Comsos Blockchains. What about non-tendermint blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum which follow Proof of Work consensus? These can be connected via proxy chain called Peg Zone. It simply tracks and copies the current state of other networks. For example, using Peg Zone created & customized for Ethereum Chain, we can send tokens from Cosmos to Ethereum and vice versa.
I hope you now have an idea how Cosmos Network works and what are its special features. It makes blockchain development easy and provides more flexibility, scalability and interoperability without compromising security. Please let me know your thoughts in the comment section below.
What is @crypto-guides?
It's an initiative by @forexbrokr to drive organic traffic to the leofinance.io domain through long-form, SEO-optimized posts featuring high-volume keywords. This project aims to eventually have a leofinance.io based crypto guide for every single coin or decentralized project in existence through user-generated content. Go and check out both the Hive guide and Bitcoin guide that they already published with contributions from the community members.
Participate & Earn Leo Tokens
You can earn crypto (LEO) by contributing to the latest guides about crypto. Learn more: https://leofinance.io/@forexbrokr/introducing-leofinance-crypto-guides




Posted Using LeoFinance Beta
Electronic-terrorism, voice to skull and neuro monitoring on Hive and Steem. You can ignore this, but your going to wish you didnt soon. This is happening whether you believe it or not. https://ecency.com/fyrstikken/@fairandbalanced/i-am-the-only-motherfucker-on-the-internet-pointing-to-a-direct-source-for-voice-to-skull-electronic-terrorism
Lately this project has caught my attention. thanks for talking about Cosmos
It is indeed a great project @stefano.massari. You are most welcome!
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta
thanks for this answer, for me it is a confirmation