Psychology: Bulimia nervosa, an eating disorder

Eating disorders are a spectrum of psychological conditions where there's an obsession with food and body shape
Bulimia is a typical example of an eating disorder. Bulimic individuals are obsessed and pre occupied with not just their body weight but their love for food thus they eat huge amounts of food for self gratification then they look for means to get rid of the excess calories they just consumed.
It is a vicious cycle of binge eating- punishing yourself for it by starving for a long time or vomiting-rewarding yourself with more food to compensate.
History
A British psychiatrist Gerald Russell in 1979 first described Bulimia nervosa
It comes from a Greek word meaning ravenous hunger.
Given the current obsession with thinness and fatophobia, you'd think that eating disorders are a relatively recent phenomena. Eating disorders have been present since time immemorial.
Bulimia dates back to the 70s where purging was used in ancient Egypt and Greco-Roman empires to prevent diseases believed to come from food.
Some early Roman emperors were observed to binge eat and subsequently induce vomiting with their fingers.
Calorie counting is a common trend especially amongst adolescent girls, when it comes to weight loss or weight maintenance, the tendency to go haywire and obsessed about counting calories is very easy.
I'd always say there's a thin line between counting calories and developing an eating disorder.
Causes and Risk factors
Being female is a risk factor
Frequent dieting and counting calories is also a risk
The exact cause is unknown but environmental and genetic factors play a role
Genetics
When one twin has bulimia, the tendency of the other twin developing it is high. First degree relatives and siblings who have bulimia also increase the chances of getting it
Personality factors
Environmental factors like traumatic events, stress
Psychological factors like depression or anxiety disorders
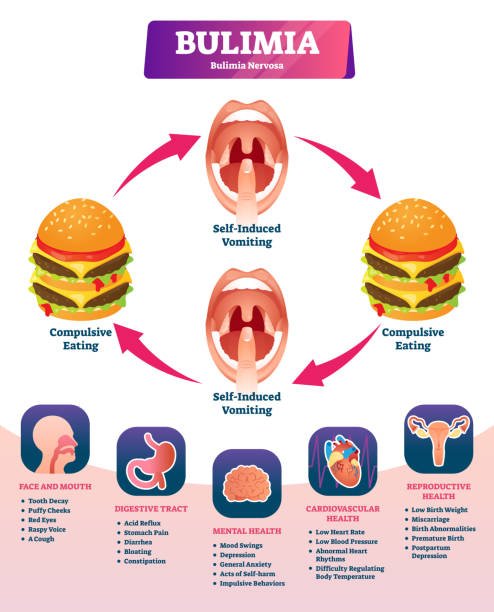
Types
Purging type
It is the commonest form of bulimia.
In this type, after the individual consumes tons of food, he resorts to using laxatives or other over the counter drugs that induce vomiting or may self induce vomiting so as to expel the food consumed. It is more deadly compared to the non purging type because these individuals come down with electrolyte imbalances which could result in death if not noticed on time.
Non purging type
The person eats a whole lot but uses other means to burn the calories like exercising or fasting for long hours.
Signs and Symptoms
Regular fluctuations in body weight
Obsession with food and lack of self control around food
Feeling guilty when eating food
Hiding to eat, eating alone or avoiding friends and family when it's time to eat
Going to the bathroom frequently during or after meals
Bad breath usually a stench of vomit
Sores and ulcers in the throat or mouth
Heart burn
Recurrent abdominal pain
Signs of dehydration like sunken eyes, dry skin, marked thirst
Poor sleep patterns
Menstrual irregularities
Swollen glands in the neck
Treatment
Acceptance that you have bulimia is the first step to treatment and the most difficult as most sufferers are in denial.
Also because of the stigma associated. Most sufferers tend to hide their condition and thus don't seek help. Talking to someone about it also key in recovery
Treatment is multidisciplinary centered round the individual involving psychiatrist, psychotherapists, dietitian and family members.
Cognitive behavioural therapy
This is a life long and continuous treatment process.
It is an effective tool in treating bulimia. This therapy involves talking to a mental health specialist. The aim is to identify negative thought patterns that led to the condition and alter them. Simply put, it's like rewiring the thought process of the person from bad to good so it takes a while and it doesn't work in everybody.
It doesn't just change the way the patient thinks about food and eating but teaches them skills they need to prevent a relapse.
Family based treatment: the family members of the sufferer are involved in this method.
Another treatment method is use medications
Antidepressants such as Fluoxetine
Nutrition education
Done by a dietitian. Care should be taken while using this modality to avoid creating more obsessions. A flexible meal plan is constructed consisting of nutritious meals and snacks, there's room for cheat days to satisfy cravings. The aim is to eliminate routine.
In patient treatment
When outpatient treatment fails and symptoms become very severe, the Individual may be admitted for close monitoring and treatment for a while
Complications
If not recognised and managed. The sufferer may have the following on the long run
Dental caries
Stomach ulcers
Barret's oesophagus
Cancer of the oesophagus
Cardiac arrhythmias or disorders in heart rhythm
Cardiac arrest
Infertility
Reduced bone mineral density